Fixed Deposits are the traditional investment choice for most Indian households. As per RBI research released in June 2020, 53% of average household financial assets are invested in Bank FDs (as on March 2020). Though mutual funds have a long
history in India with setting up of Unit Trust of India in 1963, popularity of mutual funds among retail investors have grown only in the last 20 – 25 years. As per AMFI data, AUM of mutual funds in India has grown at CAGR of nearly 17%
over the last 20 years. Despite the rapid growth, RBI research suggests that mutual funds comprise only 7% of household savings. We will compare FD vs mutual fund so that investors can make informed decision on whether to invest in FD
or mutual funds.
What are Fixed Deposits?
As the name suggests, FDs offer fixed interest rate to investors for fixed tenures. FD tenures can range from 7 days to 10 years. Bank FD interest is compounded, i.e. you get interest on accrued interest. For example, let us assume a bank
pays 6% interest (compounding annually) for 3 year FD. If you deposit Rs 100, after 1 year your account will have Rs 106. In year 2, you will get 6% interest on principal plus interest, i.e. 6% on Rs 106 or Rs 6.4. The additional 40 paisa
is due to compounding.
A cause of concern especially for senior citizens who invest their savings primarily in FDs is the declining interest rates. FD interest rate has seen secular decline over the past 25 years (see the chart below). With RBI cutting interest
rates aggressively in the wake of COVID-19 outbreak, banks have also reduced FD interest rates. On a post-tax basis, FD interest rates are now barely able to beat inflation. FD interest is taxed as per income tax slab of depositors. Since
the FD interest rate is fixed over the FD tenure, there is no indexation benefit in taxation if FD vs mutual fund comparison is done. Therefore, there is no protection from inflation, especially when FD interest rates are so low.
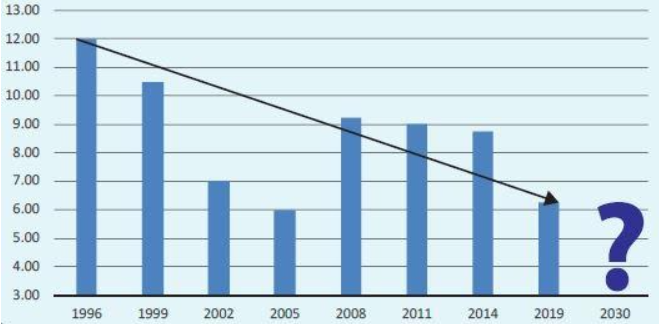 Source: Advisorkhoj Research
Source: Advisorkhoj Research What are Mutual Funds?
Mutual funds are financial instruments formed by pooling money from many investors and managed by Asset Management Companies. Mutual funds are portfolios of stocks or bonds of which unit-holders have ownership. mutual funds offer a variety of investment options based on investors’ financial needs. Equity mutual funds invest primarily in the stock market whereas debt funds invest in money and bond markets. The primary investment
objective of equity funds is capital appreciation and for debt the objective is to generate income.
While investing you should choose schemes whose fund managers have good long term performance track record. The table below shows 3, 5 and 10 year annualized returns of top performing equity and debt mutual funds.
Average performance of top quartile mutual funds
| Mutual funds | 3 year returns | 5 year returns | 10 year returns |
|---|
| Equity | 5% | 6 – 7% | 11 – 13% |
| Debt | 8 – 9% | 8 – 9% | L8 – 9% |
Source: Advisorkhoj Research. Past performance may or may not sustain in future.
One major advantage of mutual fund vs fixed deposit is taxation. Mutual funds are among the most tax efficient investments. Short term capital gains in equity funds (held for less than 12 months) are taxed at 15% and long term capital gains
(held for more than 12 months) of up to Rs 1 lakh are tax exempt and taxed at 10% thereafter.
In debt funds, short term capital gains (held for less than 36 months) are taxed as per the income tax slab of the investor and long term capital gains (held for more than 36 months) are taxed at 20% after allowing indexation benefits. Therefore,
in debt fund vs fixed deposit comparison, debt funds scores high.
Key difference between fd and mutual funds’ which has a S.V of 90.
| Parameters | FD | Mutual Funds |
|---|
| Safety | Very safe (subject to financial strength of the bank). | Mutual funds are subject to market risks. Different types of schemes have different risk profiles. Invest according to your risk appetite. |
| Liquidity | Medium to Highly liquid. Penalties may apply on premature withdrawals | Open ended funds are highly liquid. Exit load may apply for withdrawals within a certain period from the date of investment |
| Returns | Assured returns | Market linked. Historical returns track record of top performing funds across categories is strong |
| Taxation | As per income tax slab of investors | Long term capital gains tax advantage. If you compare debt fund vs fixed deposit, Indexation benefits in debt funds makes it more tax friendly for investors in higher income tax slabs |
| Investor interest protection | Regulated by RBI | Regulated by SEBI |
Safety of FD versus mutual funds
When FD vs mutual fund is compared, FDs are thought to be the safest investment because of assured interest and principal on maturity. Though FDs are thought to be risk-free investments, investors should know that the liquidity and safety
of FD depends on the financial solvency of the bank/ financial institutions. Banks are regulated by RBI, which tries to ensure prudential lending norms so that depositor’s money is safe. However, several incidents of violations of RBI
norms have been seen in the recent past leaving depositors in the lurch. Such incidents can cause suspension of withdrawal, limits imposed on how much you can withdraw and even not being able to withdraw your money indefinitely depending
on the situation. Such unpleasant incidents notwithstanding, FDs are by and large very safe and give you assured returns.
While comparing mutual fund vs fixed deposit, mutual funds diversify risks by investing in a portfolio of stocks or bonds. However, mutual funds are subject to market risks and there is no assurance of returns unlike FDs. Different mutual
funds like equity funds and debt mutual funds have different risk profiles. Equity as an asset class is much more volatile than debt funds but has the potential of high returns
over a long investment horizon compared to debt funds. Equity funds are suitable for long term investment goals while debt funds are suitable for short to medium term goals. Therefore, investors should always invest according to their
financial goals and risk appetite. Moderately high to high risk appetite profile investors can select equity funds while those who can take only moderate to low risk can invest in debt funds.
Conclusion
In this article we discussed difference between FD and mutual fund from a risk stand point. FDs give assured returns while mutual funds are subject to market risks. However, if you understand your risk appetite and invest accordingly, mutual
funds can be good investment options in a declining interest rate environment. Indexation benefits in long term capital gains taxation of debt funds, certainly give mutual funds a significant tax advantage over FDs. You should evaluate
your financial goals and risk appetite to make informed investment decisions.
An Investor Education and Awareness Initiative by Mirae Asset Mutual Fund.
For information on one-time KYC (Know Your Customer) process, Registered Mutual Funds and procedure to lodge a complaint in case of any grievance Click Here.
Mutual Fund investments are subject to market risks, read all scheme related documents carefully.
 ETF Website
ETF Website
 Invest Now
Invest Now
 Online e-KYC
Online e-KYC
![mirae asset usa]() Australia
Australia
![mirae asset brazil]() Brazil
Brazil
![mirae asset colombia]() Colombia
Colombia
![mirae asset hong kong]() Hong Kong SAR
Hong Kong SAR
![mirae asset Japan]() Japan
Japan
![mirae asset uk]() United Kingdom
United Kingdom
![mirae asset usa]() United States
United States
![mirae asset singapore]() Singapore
Singapore
![mirae asset uk]() Ireland
Ireland
![mirae asset canada]() Canada
Canada
![mirae asset india]() Global
Global
![mirae asset australia]() Australia
Australia
![mirae asset hong kong]() Hong Kong SAR
Hong Kong SAR
![mirae asset india]() India
India
![mirae asset korea]() Korea
Korea
![mirae asset korea]() UAE
UAE
![mirae asset uk]() United Kingdom
United Kingdom
![mirae asset usa]() United States
United States
![mirae asset vietnam]() Vietnam
Vietnam
![mirae asset korea]() Korea
Korea
 Global
Global
 Australia
Australia
 Hong Kong SAR
Hong Kong SAR
 India
India
 Korea
Korea
 UAE
UAE
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 United States
United States
 Vietnam
Vietnam
 Korea
Korea
 Australia
Australia
 Brazil
Brazil
 Colombia
Colombia
 Hong Kong SAR
Hong Kong SAR
 Japan
Japan
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 United States
United States
 Singapore
Singapore
 Ireland
Ireland
 Canada
Canada





 Source: Advisorkhoj Research
Source: Advisorkhoj Research